
#GGPLOT HISTOGRAMS CODE#
If you’d like the code that produced this blog, check out the blogR GitHub repository. To create a histogram in ggplot2, you start by building the base with the ggplot() function and the data and aes() parameters. Thanks for reading and I hope this was useful for you.įor updates of recent blog posts, follow on Twitter, or email me at to get in touch. Now have fun tweaking the colours! p <- ggplot(d, aes(x, fill = cut(x, 100))) + The final touches are to set the theme, add labels, and a title: ggplot(d, aes(x, fill = cut(x, 100))) + Tweak chroma and luminance with c and l: ggplot(d, aes(x, fill = cut(x, 100))) + To get your colours right, get familiar with the hue scale.įor example, here we’ll tweak the colours to range from blue to red: ggplot(d, aes(x, fill = cut(x, 100))) + Not a bad starting point, but say we want to tweak the colours.įor a continuous colour gradient, a simple solution is to include scale_fill_discrete and play with the range of hues. Oh, ggplot2 has added a legend for each of the 100 groups created by cut! Get rid of this with show.legend = FALSE: ggplot(d, aes(x, fill = cut(x, 100))) + Specifically, we fill the bars with the same variable ( x) but cut into multiple categories: ggplot(d, aes(x, fill = cut(x, 100))) + We can add colour by exploiting the way that ggplot2 stacks colour for different groups.

Time to jazz it up with colour! The method I’ll present was motivated by my answer to this StackOverflow question. Let’s simulate data for a continuous variable x in a data frame d: set.seed(070510)Ĭreate the basic ggplot2 histogram via: library(ggplot2)
#GGPLOT HISTOGRAMS HOW TO#
In this post you’ll learn how to create histograms like this: You can use boundary to specify the endpoint of any bin or center to specify the center of any bin.Pretty histograms with here to make pretty histograms with ggplot2! Make sure the axes reflect the true boundaries of the histogram.
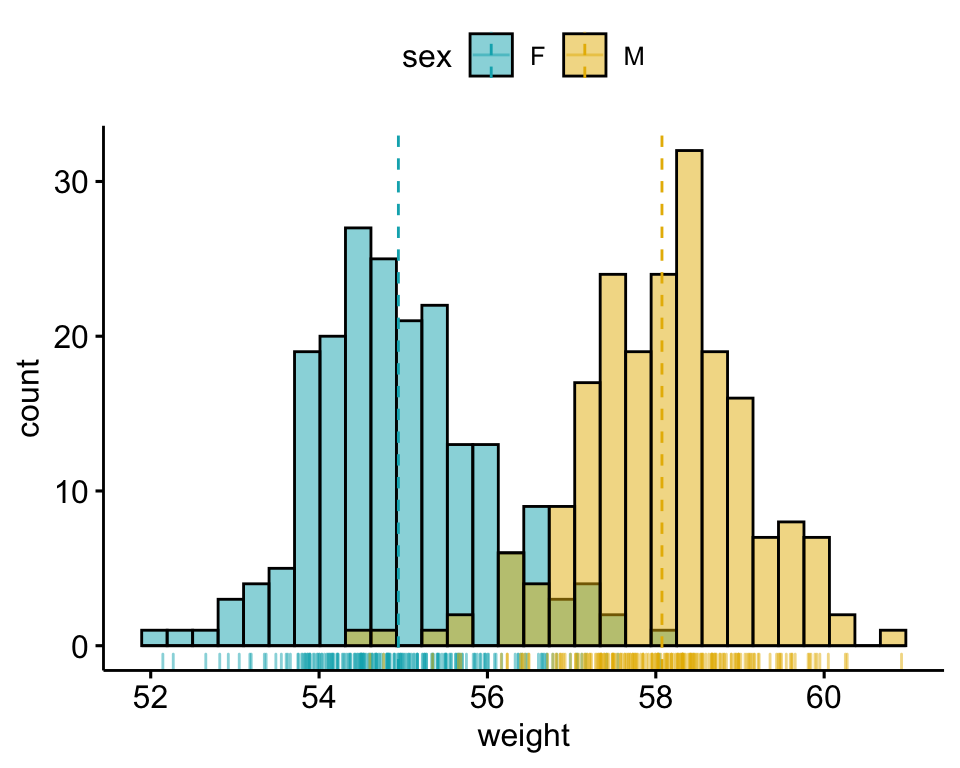
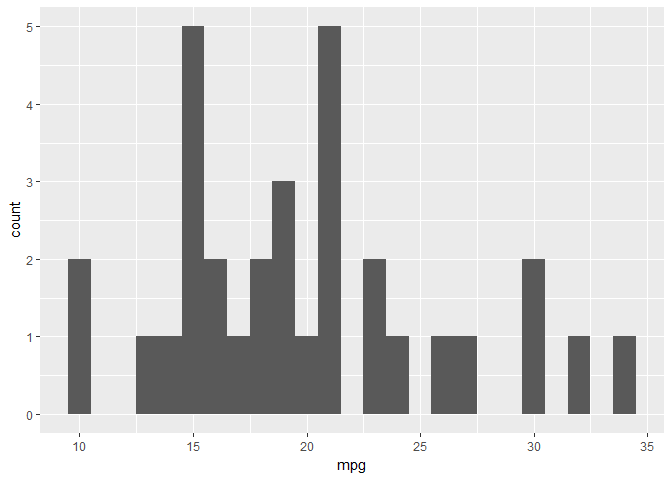
Histograms ( geomhistogram) display the count with bars frequency polygons ( geomfreqpoly) display the counts with lines. 13.6.3 Aside: example where alpha blending works Visualise the distribution of a single continuous variable by dividing the x axis into bins and counting the number of observations in each bin.13.2 Quick note on doing it the lazy way.9.3 Normal or not (examples using qqnorm).7.3.1 Adding the median and the interquartile range.
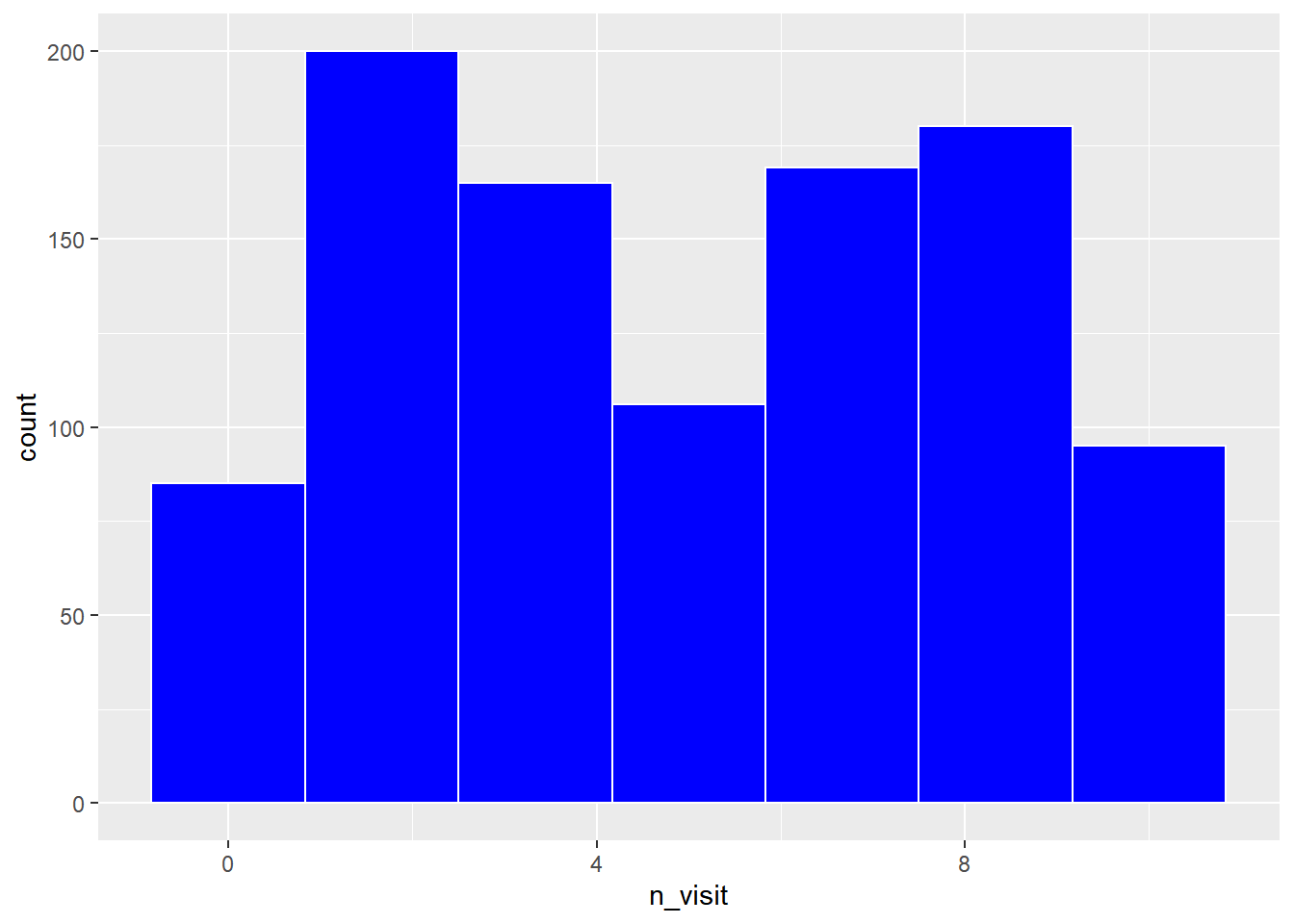
7.3 Adding Statistics to the Violin Plot.5.7.4 Change center (with data values shown).4.4.7 Last Step: Sync local master with upstream master.4.4.3 Step 3: Configure remote that points to the upstream repository (once).4.4.2 Step 2: Clone origin and create a local repository (once).4.4.1 Step 1: Fork the upstream repo (once).4.4 Ways you can contribute (need to use Git).
4.3 Ways you can contribute (Github only).3.3.5 Executive summary (Presentation-style) Visualise the distribution of a single continuous variable by dividing the x axis into bins and counting the number of observations in each bin.This document explains how to do so using R and ggplot2. A common task is to compare this distribution through several groups. 3.3.4 Main analysis (Exploratory Data Analysis) Histogram with several groups - ggplot2 A histogram displays the distribution of a numeric variable.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
